What is a nanosatellite?
It is a small satellite weighing from 1 to 24kg.
The nanosatellites developed by the CSUM are of the CubeSat type.
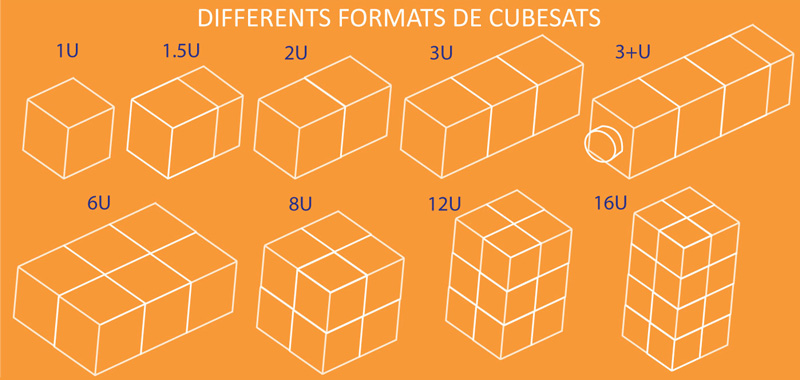
Different types of nanosatellites
CubeSats 1 Unit (1U)

Size: 10 cm edge
Masse: 1 kg
Volume: 1 Litre
Our nanosatellites orbit the Earth by spinning in a non-stabilized rotation.
They are non-manoeuverable.
These features are compatible with standard containers for CubeSats called “deployment systems” which, mounted on launchers, allow the ejection of nanosatellites into space.
Triple CubeSats or 3 units CubeSats (3U)
Size: 34.5 x 10 x 10 cm3, the equivalent of a stack of 3 1U CubeSats
Mass: up to 4 kg
Our nanosatellite can stabilise itself to direct its solar panels towards the sun, survey a point on the globe or in space and point its antenna towards the ground station.
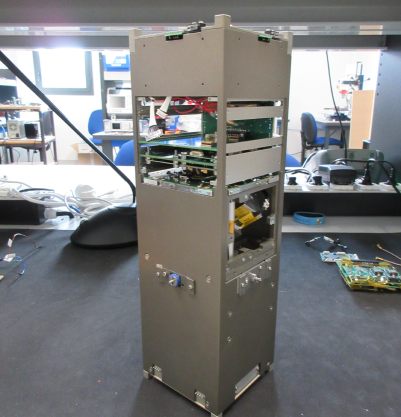

CubeSats 6 Units (6U-12U)
CubeSats 6U:
Size : 34.05 x 22.36 x 10.0 cm3
Mass : 12 kg
CubeSats 12U:
Size : 34.05 x 22.36 x 22.36 cm3
Mass : 24 kg
Our nanosatellite can stabilise itself to direct its solar panels towards the sun, survey a point on the globe or in space and point its antennae towards the ground station.
We can carry larger payloads and have more power available.
WHAT IS ITS FUNCTION?
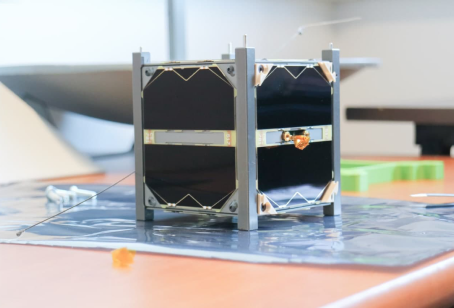
To put it simply, a CubeSat carries a scientific experiment, called a “payload”.
Everything else on the satellite that enables it to work is called “the platform”.
CubeSats are training, research and engineering tools.
They allow university students to learn about space technologies by building satellites to their own specifications and provide researchers with new research tools.